Menu

Did you know the number of farmers in the United States has been dropping? However, agricultural output is actually rising. This shows how technology is changing farming. By 2024, both agriculture and the freight industry will change even more. The U.S. exports over 20% of its agricultural goods every year. So, it’s vital to know the latest trends and forecasts for stakeholders.
It’s interesting that the costs to grow major crops like corn and soybeans are set to fall in 2024. This decrease could be between 1.4% and 3.6% from the year before. Also, the interest rates per acre might fall by about 30%. Plus, the cost of fertilizers could be 17% lower. These changes show how the agricultural market is always changing. They also suggest farm owners might face less financial pressure. As we move into 2024, let’s look at how these shifts will impact the freight industry. This sector plays a vital role in moving agricultural goods worldwide, where demand is growing.
As we near 2024, agriculture remains the world’s economic heart. It is responsible for providing necessary items to people globally. I will explore key global agriculture market insights here. We will look at past trends to predict future freight sector changes.
In 2024, farm incomes are expected to fall. Net farm income may drop by $39.8 billion, down 25.5% to $116.1 billion. Net cash farm income will also decrease by $38.7 billion to $121.7 billion. Adjusting for inflation, there could be a $43.1 billion decline.
Production costs are projected to rise by $16.7 billion to $455.1 billion. At the same time, farm sector equity could go up by 4.7%, reaching $3.74 trillion. Assets in the farm sector might increase by $193.2 billion to $4.28 trillion.
Farm sector debt may rise by 5.2%, hitting $547.6 billion. The median farm household income is expected to drop to $99,445 in 2024.
Crop cash receipts are set to decrease by 8.3%, or $22.4 billion. Animal product cash receipts might also fall by 4.0% ($9.9 billion), reaching $239.8 billion. This shows the need for sustainable practices and smart planning within crop price projections.
These details give a broad look at how agriculture is changing. It stresses how crucial it is to follow farming market trends closely. Knowing these trends can help stakeholders tackle what 2024 will bring.
Agriculture is changing thanks to new technologies. Modern tools have made farming more efficient and precise. This allows farmers to get better yields using fewer resources. I will talk about some areas where technology is making a big difference in agriculture.
Drones are now a key technology in farming. They help keep an eye on the health of the soil and crops. Drones can find pests and diseases. They also help with putting out pesticides and fertilisers. This means farmers don’t have to spend as much money or time checking fields. Drones give them up-to-date and accurate information. This helps in taking care of crops in the best way.
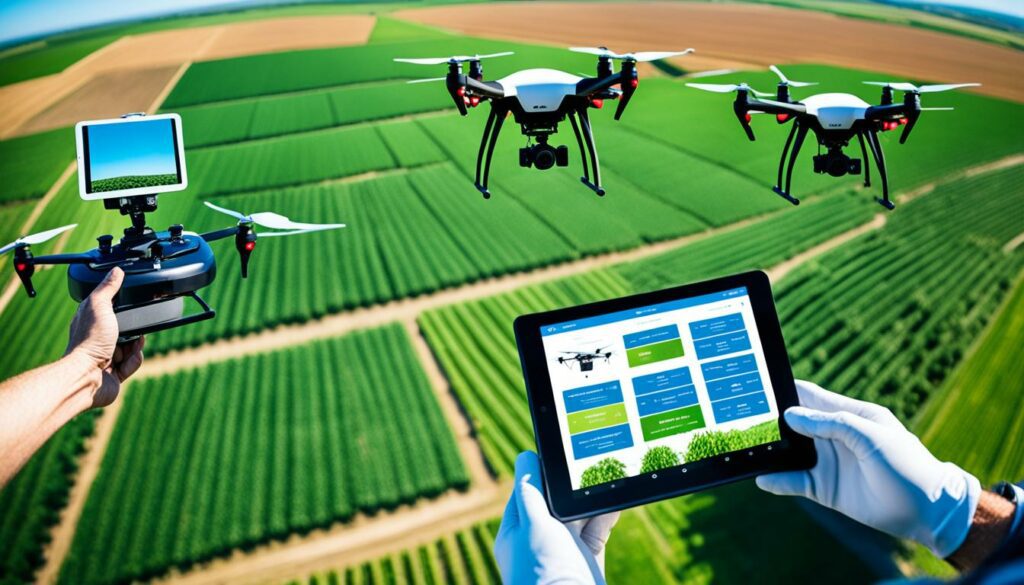

The use of GPS, sensors, and remote sensing is changing how we manage crops. These technologies let farmers use things like water and fertilisers more precisely. By looking at soil, weather, and crop data, they can come up with plans just for their fields. This makes farm work more efficient and effective. Studies show that these technologies will change farming a lot in the future.
| Technological Advancements | Impact on Agriculture |
|---|---|
| Drones in agriculture | Real-time monitoring, reduced field trial costs |
| Precision agriculture | Enhanced resource efficiency, tailored solutions |
| Remote sensing | Accurate data collection, climate adaptability |
| Autonomous farm vehicles | Reduced labour costs, increased productivity |
Self-driving farm vehicles are changing the game. With these vehicles, there’s less need for workers. This makes farm work more efficient. It also lets farmers focus on making big decisions and managing their farms. Using autonomous vehicles is lowering costs and making farms more productive. It is a big step forward in farming technology.
To sum up, technology like drones, precision agriculture, and autonomous vehicles is shaping agriculture’s future. This tech makes farming better, easier, and more sustainable. Its impact will only grow in the coming years.
The USDA promotes a mix of conventional and organic methods in farming. While 90% of farmers know about these ways, they only use them on a small part of their land. Key techniques include not breaking the soil, using fertiliser where it’s needed most, and watering carefully.
Programmes led by the government are more popular (used by 57%) than those from within the industry (chosen by 4%). Even though 74% of farmers know about making energy on the farm, just 13% take it up. They hope to increase their harvests and land’s worth by farming more sustainably, even if it costs them a bit more.
Help with changing how they farm is very important. Smaller farmers, those with less than 200 hectares, find it hard to try no-till ways due to money issues. But, using soil samples to apply fertiliser is seen as a very good investment. Growers of special crops are more into these green ways than those who grow typical crops.
The farming world must change to help the climate, as it puts out a lot of the world’s greenhouse gases. For solutions, efforts like the COMET Planner from Colorado State University help farmers see how they can store more carbon. This work goes with the USDA’s mission to give local, science-based tips for fighting climate change.
All these points show the need for more farmers to go green. It’s crucial for feeding the world while caring for our planet for the future.
The climate change effects on agriculture are clear, with weird weather patterns messing up farming. This leads to new challenges. Scientists have come up with a new way to look at past climate info and the effects on crops. They found that the future is risky for farming. They say we need to change how we do things now.

Weather pattern disruptions are a big deal caused by climate change. By 2050, northern Brazil will have bigger changes in seasons. It’ll be wetter in winter and drier in summer. Meanwhile, areas like central Brazil will get hotter. This means we’ll need crops that can handle the heat. In Brazil, 7% more farmers might not be able to pay back loans because of these changes. This shows us how big the impact on farming is.
In the United States, corn yields are predicted to go up by 3.1% by 2036. It’s not a big increase compared to before. But, soybean yields are expected to drop by 3.0% in the same period. States like Illinois, Missouri, Iowa, and Wisconsin will be affected differently. The crops there will change because of the weather.
It’s key for farms to have mitigation strategies to keep going strong. A study has looked into how climate change will affect different places and parts of farming. This info is super helpful for organisations that depend on steady farm produce.
The research can help government and policymakers. It tells them how the local climate will change. Then, they can decide if local, national, or global groups are best to handle these changes. Figuring out where investments make the most difference is vital. This includes looking at the loss and damage fund set up by the United Nations in 2022.
| Region | Corn Yield Change by 2036 | Soybean Yield Change by 2036 | Climate Challenge |
|---|---|---|---|
| Central States (US) | -14.5% | -7.1% | Increased temperatures |
| Illinois, Missouri, Iowa, Wisconsin | +5.7% | +1.2% | Variability in rainfall |
| Northern Brazil | Not specified | Not specified | Heavier winter rains, drier summers |
To deal with the climate change effects on agriculture, we need to get proactive with our agricultural mitigation strategies. Planning wisely and improving our infrastructure is crucial. It will help us face and reduce the effects of weird weather.
The global food supply chain is like a puzzle that’s key to filling the world’s plates. It’s under pressure due to the growing population, set to hit 9.7 billion by 2050. This upsurge strains agricultural productivity and the network that distributes food. Knowing how food demand and supply chain strength are linked is vital. It helps keep farming running smoothly and ensures everyone has enough to eat.
More people mean we need more food, which has a big effect on farming. The growing demand worldwide is clear in the rising cost of food, up 2.2% between March 2023 and March 2024. To meet this demand, we need better ways to grow food and use our resources. Technology is key here. Things like smart farming and technology in agriculture are on the rise. By 2024, almost 300 million of these tech devices will be in use.
The pandemic showed how vital it is to have strong food supply chains. It pointed out weaknesses and reminded us to be ready for anything. Food costs, especially those in restaurants, went up 4.2% in the year to March 2024. To make the supply chain stronger, we must improve how food moves and add flexibility at every step. This is crucial as world events and disruptions can hike up the cost of making and moving food.
| Category | Price Change (Feb to Mar 2024) | Year-over-Year Change (Mar 2023 to Mar 2024) |
|---|---|---|
| All Food | 0.1% | 2.2% |
| Food-at-Home | 0.0% | 1.2% |
| Food-Away-from-Home | 0.3% | 4.2% |
| Beef and Veal | 0.7% | 7.6% |
| Pork | 1.2% | 0.3% |
| Poultry | 1.5% | 2.1% |
| Fish and Seafood | 0.3% | -2.6% |
| Retail Eggs | 0.2% | -6.8% |
| Dairy Products | -0.4% | -1.9% |
| Fresh Fruits | -0.5% | n/a |
| Fresh Vegetables | -0.6% | n/a |
In wrapping up, agriculture is changing fast to meet our rising food needs. It’s full of new ideas and investments to make supply chains stronger. This shift is critical for facing the increased demands and the tough road ahead.
Today, the cost of production updates are essential for farmers. Costs for crops and livestock care have topped $460 billion in 2023. This marks a 28% jump from 2020. It shows how crucial planning and watching costs closely are for farm success.
The outlook for key crops is mixed, but generally positive. The costs for corn, soybeans, and wheat are expected to slightly decrease. For example, the expected cost for producing corn per acre in 2024 is $856. This is down by 3.6% compared to the last year. Soybean costs are expected to reduce to $613 per acre by 1.4%. Wheat is projected to have the lowest cost per acre in 2024 at $416 after a 2.3% cut.
| Crop | Cost of Production in 2024 ($/acre) | % Change from 2023 |
|---|---|---|
| Rice | 1,200 | -1.8% |
| Peanuts | 1,172 | -1.6% |
| Cotton | 866 | -1.6% |
| Corn | 856 | -3.6% |
| Soybeans | 613 | -1.4% |
| Wheat | 416 | -2.3% |
Looking into input costs, some expenses are set to go down, while others will rise. Interest costs per acre are expected to drop by 30% from 2023 to 2024. Also, fertiliser prices will decrease by 17%. But, the costs for seeds, labour, and machinery are estimated to increase. It makes the overall financial picture complicated for major crops.
Agriculture has to deal with these cost changes to stay profitable. The rises in fertiliser, financing, and fuel costs have made the past years more expensive. Farming must be managed carefully to reduce the impact on earning.
So, the future’s cost mix calls for very strategic management. This ensures a strong and profitable path for agriculture ahead.
Digital agriculture is changing how we farm, bringing new and exciting technologies. The market was worth USD 21.72 billion in 2023. By 2031, it’s set to reach USD 51.35 billion. This shows the big role of things like drones, IoT in farming, and using data in agriculture today.
One big part of this growth is in precision agriculture and managing farms better. It’s leading the market since 2022. The use of IoT devices in farms and high-tech field equipment is pushing this field forward.
Big players like Cisco, IBM, and Deere & Company are driving forward with new tech. They’re making farming smarter with IoT tools, making real-time gathering and studying of data better. This helps farmers monitor crops closely, and make quick decisions to improve their harvests.
North America is a key area for this new tech in farming. By 2024, about 60% of farms there will use digital farming methods. They plan to spend more on precision tools and double their use of IoT devices. This shows how much they believe in these new approaches.
There’s big promise in new types of software for farm management, with a CAGR of over 12%. Large farms are expected to use this kind of software by 70%. It will make running farms smoother and more efficient.
Smart irrigation and drones are also changing farming quickly. Smart irrigation is expected to grow by 15% each year until 2024. The use of drones in farming will grow by 30% in three years. These technologies are making agriculture more digital.
Using data and tech is making farms work better and grow faster. By 2024, these digital tools in farming will grow by 20%. This shift is transforming farming across the world, making it more efficient and productive.
Regenerative agriculture is changing the face of farming for the better. It focuses on making soil healthier, boosting biodiversity, and helping ecosystems cope better. The approach is catching on worldwide, with top businesses and smart strategies backing it up.

Adaptive grazing leads the way in regenerative farming. It uses planned animal grazing to keep pastures healthy. This helps new plants grow, keeps the soil safe, and it all adds up to better soil and water.
No-till farming is now a key part of looking after the land. By not ploughing, farmers keep the soil structure. This stops erosion, helps water soak in, and traps more carbon. It’s a strong move towards a sustainable future supported by farmers and big businesses.
Using fewer chemicals is a key step in regenerative farming. It means the soil is happier, and crops can fight off pests and disease better. Big brands like Cargill and PepsiCo are leading the way in these changes. They aim for greener farming that also makes economic sense.
Here’s an overview of how regenerative agriculture is expanding:
| Market Segmentation | Details |
|---|---|
| Growth Projection | US$ 5,710 million by 2034 with a CAGR of 15.6% |
| Top Companies | Nestle, Bayer, Danone, Cargill, PepsiCo, General Mills, Understanding Ag, ADM, Walmart, Syngenta, McCain Foods, Wikifarmer, Kering, Fai, Balboa Group, Esri |
| Market Segments | Enterprise, Self-Employed; Agriculture, Animal Husbandry, Others |
| Opportunities | Consumer recognition, improved soil fertility, reduced costs, innovation |
The regenerative farming movement is getting big, especially in South Korea and the United States. And agroforestry is on the rise too. These methods look after our planet and help farmers economically. It marks a big change in how we farm for the future.
The agricultural biotechnology market is growing like never before. It’s set to almost double from USD 28,587.7 Million in 2022 to around USD 59,721.3 Million by 2030. This boost is moving at a rate of 9.7% a year, thanks to many new ideas and smart moves.
Recently, crop management innovation has taken the spotlight in agricultural biotechnology. Advancements like digital twins and generative AI are starting to show up in farm plans. They allow for keeping an eye on things in real time and predicting future trends. This helps farmers choose the best actions based on solid data. It all plays a big part in meeting the world’s ever-growing need for food.
The use of genetic engineering in farming is very important. With the latest agricultural biotechnology developments, advanced gene-editing techniques like CRISPR are available. These methods let experts tweak crop DNA very precisely. They help in making crops that stand up better to changing climate, pests, and diseases. Also, new types of biostimulants and biofertilizers are making old farming ways better. They increase crop harvests and keep the soil healthy.
| Region | Market Value (2022) in USD Million | Projected Value (2030) in USD Million | Key Countries |
|---|---|---|---|
| North America | 8,764.3 | 18,314.7 | United States, Canada, Mexico |
| Europe | 7,658.9 | 15,992.3 | Germany, UK, France |
| Asia-Pacific | 6,422.6 | 13,527.5 | China, Japan, India |
| South America | 3,881.2 | 8,022.8 | Brazil |
| Middle East and Africa | 1,860.7 | 3,864.0 | GCC Countries, Egypt |
Smart farming is transforming agriculture around the world. It uses the Internet of Things (IoT) to make farming more automated and efficient. Market reports show that in 2023, the “IoT in Smart Farming Market” was worth USD 20.5 billion. It’s expected to grow to USD 54.4 billion by 2031, with a steady growth every year.

Technologies like the IoT, AI, and robotics are changing how farms work. This leads to better crop yields and more sustainable farming practices. The United States is a key player, thanks to its advanced tech and big investments in farm automation. In Europe, the stable economy and high tech use also make it a fast-growing market.
This market is divided into types and uses, helping companies plan better. Big names like Cisco, IBM, and John Deere are leading the way. By looking at market data from different regions, we can spot trends and new opportunities.
| Region | Market Share (%) | Main Players |
|---|---|---|
| North America | 40% | Cisco, IBM, John Deere |
| Europe | 30% | Trimble, Virtus Nutrition |
| Asia-Pacific | 20% | KaaIoT Technologies, Oracle |
| Others | 10% | Various |
As IoT technology improves, farming will get better and more varied. North America and Europe will lead this growth, bringing more innovations to farming.
The high cost and knowledge needed for IoT can be challenges for farmers. Data privacy and security are also concerns. Yet, partnerships like IBM with the Government of Gujarat show efforts to overcome these challenges.
With the IoT, the future of farming looks bright. Advancements in smart farming move us closer to sustainable and efficient agriculture.
The link between being economically strong and sustainable in farming is clear. An economy that can last in agriculture must make money while looking after the future. This balance is key for the field to keep growing.
It’s vital to keep the land healthy and productive for the long run. We must take care of the environment. This is especially true today because we might see farm incomes drop by a lot.
Experts predict that between 2023 and 2024, there may be a 25.5% less money coming in, going from $155 billion down to $116 billion. This could be the most significant drop ever in one year. With inflation considered, the drop could be even worse, sitting at about 27%. This shows why working in a way that lasts is so important.
The market effects could be big, with farmers possibly getting less money for their goods. At the same time, spending might go up, making things even tougher. This situation calls for strong economic planning to soften these blows. The support from the government might also decrease, making things harder for many.
For instance, payments that help when unplanned things happen could go from $5.49 billion down to $0 in some cases. The fall in earnings from selling crops and animals, along with the cost of running a farm going up, are serious challenges. Projected scenarios show drops in areas like corn by 14%, which is a big financial hit. The need for smarter spending is clearer than ever.
New ways to fund farming emerge, highlighting the Organic Agriculture Research and Extension Initiative and the Rural Business Development Grant Program. These aim to help small and starting farms be stronger and more sustainable. Their role is vital in tough times like these, supporting a healthier agricultural economy.
The international agricultural trade scene is always changing. It’s heavily influenced by global happenings. In 2023, even though the world economy grew by 2.7%, trade in goods dropped by 1%. This shows a hard time with more protectionism, issues with travel routes, and difficulties from global issues and climate change.

Debts that countries owe have seen a big change, moving from getting money to being out nearly $90 billion. This change affects how markets are controlled globally.
Food prices in dollars have fallen, but this hasn’t helped everyone. The prices are still going up in many places, making it hard for people with low incomes. In 2022, almost half of the developing countries got into more debt than they could handle.
The UN agency for trade and development expects things to get harder in 2024. This is because investments are dropping and global trade is slowing down. Merchandise trade around the world might not grow as much, but the service sector might do a bit better.
| Year | GDP Growth | Merchandise Trade Volume | Commercial Services Trade |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 2.7% | -1.2% | +9% |
| 2024 (Proj.) | 2.6% | 2.6% | N/A |
| 2025 (Proj.) | 2.7% | 3.3% | N/A |
In 2023, the trade in goods worldwide fell by 5%, reaching $24.01 trillion. On the other hand, service trade increased by 9%, hitting $7.54 trillion. This boost in services helped make up for the loss in goods trading.
Each region also impacts how trade happens. Europe, for example, saw less demand for imports. Russia’s exports dropped by 28%, and there were big decreases in China, Japan, and South Korea. But, exports in the European Union did go up by 2%, although trades within the EU fell by 1%.
Looking ahead, the future of global trade is not clear. Big issues like global tension and policy changes could make things even harder. But, some hope comes from a prediction of lower interest rates in 2024. This could help reduce financial pressures worldwide.
The alternative proteins trend is making big changes in how we farm. It’s all about the growing love for plant-based nutrition and lab-grown meat. This change is part of a big move to make food more sustainably around the world.
People are getting more into plant-based proteins. They’re not just good for the planet but also for our health. Half of us are picking healthier foods, according to a recent survey.
This has led to more crops like soybeans and legumes being grown. These crops are great for helping out in the protein department. Plus, they give a chance for new farming technologies to shine.
Lab-grown meat aims to hit a $25 billion market by 2030. It’s seen as a big leap in making food that cares for our Earth. About a third of consumers think this way too.
Start-ups are cashing in on this up-and-coming tech, and Asia’s leading the charge for eco-friendly food. This lab-meat revolution is making waves globally.
The shift to alternative proteins is changing how we use our land. More farmers are planting things like pulses and chickpeas, rich in protein. This helps meet the growing demand for plant-based nutrition.
It’s also making farming more sustainable, giving our food chain a boost. The world is asking for more fish and shellfish too, seeing a need for varied protein sources.
| Trend | Impact | Opportunities |
|---|---|---|
| Plant-Based Proteins | Healthier eating patterns | Cultivation of soybeans and legumes, agtech innovations |
| Lab-Grown Proteins | Sustainability aligns with consumer priorities | Pioneering lab-grown technologies, substantial market growth in Asia |
| Cultivation Pattern Changes | Emphasis on sustainable farming | Diversification of protein sources, resilience within food value chain |
The link between alternative proteins and farming is changing how we see food production. Consumers are choosing greener food options. This trend is paving the way for more innovation in agriculture.
on the burgeoning trend of alternative proteins and its global impact.
The agricultural market insights for 2024 show a world changing with new technology, a focus on being green, and money moves. Farm incomes are expected to fall by 25.5%, hitting $116.1 billion. Net cash income faces a cut, down 24.1% to $121.7 billion. These figures tell us farm businesses need to find new ways to make money.
Farm bills are going up by 3.8% to $455.1 billion, which makes saving resources even more vital. While farm wealth is growing by 4.7%, reaching $3.74 trillion, the debt of the farming world will climb by 5.2% to $547.6 billion. This shows how hard it is to grow, be responsible, and expand the land all at once.
On the customer side, food is getting more expensive. The cost of food went up by 0.6% from February to March 2024, and by 3.5% in one year. At the same time, prices for eating at home and out are also rising, showing inflation is here. But, with new tech in the farming world, like smart farming and machines that work without humans, there’s hope. These tools can make farms more efficient, help the planet, and face future challenges.
In 2024, agriculture will see a big push towards more tech. This means using digital tools and machines to farm better. The focus will be on saving the environment and meeting what consumers want.
Sustainability is key in farming to keep it going for years to come. It also helps fight climate change and keep our resources safe for the future. The USDA is working to mix traditional and new farming ways for good outcomes.
Technology is changing farming today in very big ways. From drones for watching crops to GPS planning, it all helps farmers do better. These new tools save time and money, making farms more productive.
Smart tech also helps cut down on harming the environment.
Farmers are tackling climate change by finding ways to keep growing food well. This includes using better farming methods and planning for strange weather. By being smart and ready, farms can keep giving us food.
They are also making sure food gets to us on time, no matter what.
In 2024, growing crops like corn and wheat will cost about the same as this year. Most of the costs will stay high, like for seeds and the machines that help farmers. But, there might be fewer bills to pay for land and loans.
Farmers need to be careful with the money they spend to make a good profit.
Diggingital farming is changing how we grow food with real-time data. Devices like drones and robots are helping farmers do things more carefully and quicker. This leads to better crops, less waste, and friendlier farming for our planet.
Regenerative farming makes the soil and the environment healthier. It helps more plants, animals, and bugs live together. By not using harsh chemicals and farming in smart ways, the land can keep making food for a long time.
This type of farming also helps take extra carbon out of the air, which is good for fighting climate change.
Agriculture is using more and more high-tech biology to grow food better. This includes picking genes to make plants stronger and using new ways to help plants grow. These high-tech tools and smart farming can make sure there’s plenty of food for everyone.
They are also good for the environment, using up fewer resources.
Smart farming uses the latest technology to do farm work better. This not only helps grow more food but also does it in a way that doesn’t hurt the planet. It means less waste and looking after animals in the best ways possible.
Money and looking after the planet are getting linked closely in farming. This is because people want food grown in ways that are kind to the earth. These new ways of farming are good for the long haul and for the environment.
They are a big change for farming, making sure it keeps being good at making food and protecting our world.
How food is sold around the world depends on many things, like politics and big health issues. Especially with events like COVID-19, making sure we keep getting food is very important. Having good plans for selling food helps us have enough to eat, no matter what.
By being ready and smart, we can make sure there is always food on our tables.
More people are choosing different kinds of protein, not just meat. This is changing what farmers grow, focusing more on plants used for protein. It shows how what we eat is changing, which affects what farmers do.
Farmers are growing more crops like soybeans and peas to keep up with what people want to eat.