Menu
By 2030, a single farm will produce over two million data points daily. This shows how important data analytics are in farming. They make farmers’ decisions smarter. Using farm data analytics, farmers can pick the best moments to plant or harvest.
They look at things like weather, soil, and crop health. This helps them get more crops and use fewer resources.
Today, farming relies a lot on data to stay successful. With the world needing more food, smart decisions are key. Agricultural decision-making using data is vital. It makes sure farms are strong and effective.
Over the years, farming has changed a lot. Now, farms use data and modern technology in new ways. These changes have moved farms from old methods to using high-tech solutions. This shift is making farms work better and be more successful.
Farming has gone from using hands and simple tools to using big machines and high-tech methods. Today, around 80% of farms worldwide use modern techniques like GPS for tractors and drones. These methods help farms produce more but also cause some problems, like the loss of many insect species.
This change shows the challenges of making farming more productive while taking care of the environment.
Data is now essential for farming. It helps farmers use their resources better. Experts in managing big data can look at how water, fertilisers, and energy are used. They then suggest ways to farm more sustainably.
Today, farming uses data for many things, from planning and predicting crop yields to checking market trends. The use of data is growing, as shown by the USDA. They found small family farms are going down by 4%, while big farms are going up by 6%. Farming with data means farmers get up-to-date information on their crops, the weather, and what’s happening in the market. This helps them make better decisions in the complex world of farming.
In today’s farming, using data for decisions is key. This way, farmers make choices based on facts, not guesses. They aim to use data to decide well for more crops and to care for the land.

This approach involves gathering and studying data from many sources. These sources might be old farm records, upcoming weather, or details about the soil and crops. By looking at this data, farmers can plan their work better and fight against risks. They use high-tech tools to predict how well crops will do and to keep the soil healthy. Doing this helps make the most of what the farm has and use resources well.
Using data helps farmers know more about their crops. Devices like sensors and drones give instant updates on plant health. This keeps the crops in good shape.
Also, data analysis helps deal with dangers like bad weather or pests. High-tech methods can spot these problems early. They also make guessing about future crops more accurate. This means using resources smartly and lowering risks.
In some places, using data in farming has shown big improvements. It has led to better choices, saving resources, and being ready for hard times. The good results of using data in farming show it’s worth the effort.
In modern farming, there are three key types of data: weather, soil, and crop data. These are vital for making wise farm decisions. They help boost productivity, sustainability, and manage risks well.
Weather data includes temperature, rain, humidity, wind speed, sunlight, and air pressure. It deeply affects how well crops grow and the amount you might harvest. With this info, farmers know the best time to plant or harvest.
Soil info is crucial for understanding what plants need. It talks about soil texture, structure, how much organic matter is there, nutrients, water holding, and pH. By studying this, farmers can use the right amount of fertiliser and water. This helps their crops and the soil to stay healthy.
Tracking crop data means keeping an eye on how much you produce, knowing if the plants are healthy, and when they grow. This info is key in finding and fixing problems early. It also helps plan for better yields in the next season more accurately.
Using all these data in farm management can do wonders. It makes analysis and decision-making sharper, improving farming methods and overall productivity. For today’s farmers, knowing about weather, soil, and crop data is crucial. They help in running farms efficiently and sustainably.
New technology has changed how data is collected in agriculture. Now, farmers use things like agricultural sensors, drones for farming, and satellite images. These help them map and monitor their land very accurately. Each new way of collecting data has its own special benefits for farmers.

In today’s farming, sensors are key. They check on important things like how moist the soil is, the air’s temperature, if leaves are wet, and how much it’s raining. These sensors send their findings straight to computers. This helps farmers make smart choices to grow more and keep things Earth-friendly. Knowing the pH of soil or how much organic matter it has can help farmers grow plants better.
Drones have made a big difference for farmers. They fly above fields taking pictures with special cameras. These clear images show where crops might be struggling. Drones help make farming very precise by keeping close eyes on the health, growth stages, and amount of crops. This means farmers can quickly fix any issues and save resources.
Looking at the earth from space helps too. High-up satellites take pictures that show a lot about fields. They tell us how plants are doing and show issues like changes in climate. With this data, farmers can plan better and take good care of their land. Using special databases, this satellite information helps farmers understand and use their data in clever ways.
| Data Collection Method | Advantages | Parameters Measured |
|---|---|---|
| Agri Sensors | Real-time data, precise measurements, wirelessly transmitted | Soil moisture, air temperature, leaf wetness, rainfall |
| Drones | High-resolution imagery, precise mapping, crop stress detection | Crop health, phenology, yield monitoring |
| Satellite Imagery | Comprehensive land views, vegetation index, large-scale monitoring | Environmental variabilities, vegetation index |
In today’s farming, bringing together data from different sources is key. This step allows you to make real use of the information. Data integration makes sure data in various formats, like JSON, XML, and CSV, work together smoothly. It keeps your data consistent and easy to handle in systems like PostgreSQL databases.
Before you can analyse it, cleaning data is a must. Methods like outlier detection and imputation are used. By cleaning the data, you get rid of mistakes and odd bits. This makes your further analysis more trustworthy.
Getting data together from sensors, drones, and satellites works well with accurate integration. For instance, sensors check the soil’s moisture and the air’s temperature. Drones take special pictures for checking the crops, and satellites give very detailed images. But, all this data must be cleaned first. This helps to make sure it’s all accurate and uniform.
To sum up, merging and purifying agricultural data with advanced tools is crucial. It helps farmers make better decisions, boosting their farms’ success.
Farmers today use predictive analytics to predict future trends and make smart decisions. It combines statistics, machine learning, and data mining. This gives farmers a full picture of their operations.
Predictive analytics looks at past data to find trends and predict future results. Algorithms and mathematical models make these predictions accurate. It helps farmers take steps before problems arise. They look closely at weather, soil, and plant health to decide wisely.
One key use of this is to forecast crop yields. Farmers study past yields and add today’s info to better use things like water and pesticides. This leads to more sustainable farming. They also use up-to-date weather data for irrigation and pest management.
For picking the best crops to grow, predictive analytics is also vital. It uses data to find crops that do well in certain climates. This boosts crop success and farming’s future.
But, predictive analytics does more than just yield predictions. It helps with market trends and using farm equipment better. This keeps farmers informed and their farms running smoothly.
Machine learning is now key in modern farming, enhancing crop yield predictions. It does this by spotting patterns in farm data for more accurate forecasts. This helps make better decisions for growing crops.
Today, precision agriculture is growing fast. It aims to boost crop production while saving water and fertiliser. It uses IoT sensors to monitor soil and climate, which improves how crops grow.
Machine learning is changing how we make choices in farming. It collects and analyses data for accurate predictions on crop growth and quality. It uses satellite images, drones, and sensors to give detailed maps to improve farming methods.
It’s also great at guessing what crops will sell well, looking at market trends and environmental conditions. And it checks crop quality, ensuring better produce reaches the market. This is all done by analysing colour, texture, and shape.
Though there are some challenges, like preparing data and high sensor costs, the benefits are clear. As more farms adopt this technology, its value continues to grow. Different algorithms, including Decision Tree and Random Forest, work well for predicting crops and maximising yields.
| Algorithm | Application | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Decision Tree | Crop yield prediction | Easy to interpret |
| Naïve Bayes Classifier | Crop quality analysis | High efficiency |
| Support Vector Machine (SVM) | Predicting crop demand | Accurate classification |
| Random Forest | Yield optimisation | High accuracy |
Machine learning techniques are improving crop predictions and quality. They help in selecting the best crops and marketing strategies. Though more research is needed, machine learning shows great promise for the future of farming.
Knowing the risks in farming is vital for its success. Today, farmers can use data analytics to spot, measure, and lower these risks.
Farming deals with many risks, from the weather to pests and market changes.
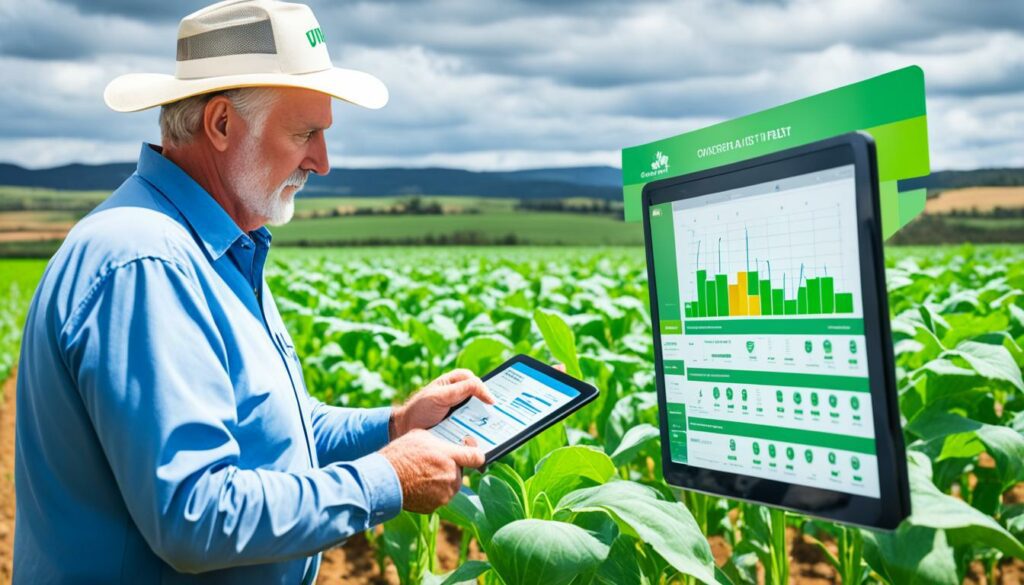

The weather, like too much rain or droughts, can hurt crops. Pests and diseases can also cause big losses. Changes in market prices affect how much money farmers make.
Using data insights is key in managing farm risks. Farmers look at info like weather, soil, and crop health to make smart choices.
Weather data shows things like temperature and rainfall. This helps predict the weather and plan ahead.
Soil data tells farmers about nutrients and pH levels. Knowing this helps grow better crops. Crop data shows how plants are doing. Early signs of trouble can be spotted this way.
Advanced methods like statistical models and machine learning are also used. These help predict future risks by studying patterns and relationships in the data.
Using these tools, farmers can adjust their farming methods. This makes their farms more stable and profitable.
| Risk Type | Analytical Method | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Weather Events | Statistical Modelling | Climate-resilient Crops |
| Pest Infestations | Machine Learning | Integrated Pest Management |
| Market Volatility | Big Data Analytics | Supply Chain Optimisation |
Data analytics is changing the game for farming. It makes farming safer and more profitable in the long run.
In Kansas, a large wheat farm used big data analytics. This led to a big increase in crop yields. It shows how important it is for farmers to use data to make smart and quick decisions.
In California’s wine country, a vineyard cut down on pesticide use. This was achieved by using agricultural data. This example proves that using data in farming can help the environment.
Also, a coffee plantation in Brazil improved its productivity with big data analysis. This means that using data can help different types of farmers, not just wheat or grapes growers.
By predicting weather and pest patterns, farmers can deal with risks better. But, there are still some challenges. For example, collecting data is not the same everywhere. Also, there are worries about keeping the data safe and private. Addressing these problems is key to making data-driven farming more widespread.
| Location | Application | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Kansas (Wheat Farm) | Big Data Analytics | Increased Crop Yields |
| California (Vineyard) | Data Analysis | Reduced Pesticide Usage |
| Brazil (Coffee Plantation) | Big Data Analytics | Maximised Productivity |
These stories show how data is improving farming. It makes farms more productive and kinder to the planet. As we use data more, farming around the world will get better.
Data analysis is changing agriculture. It allows farmers to understand a huge amount of data to make better decisions. By 2030, a farm may generate over two million data points every day. This shows the power of big data in farming.
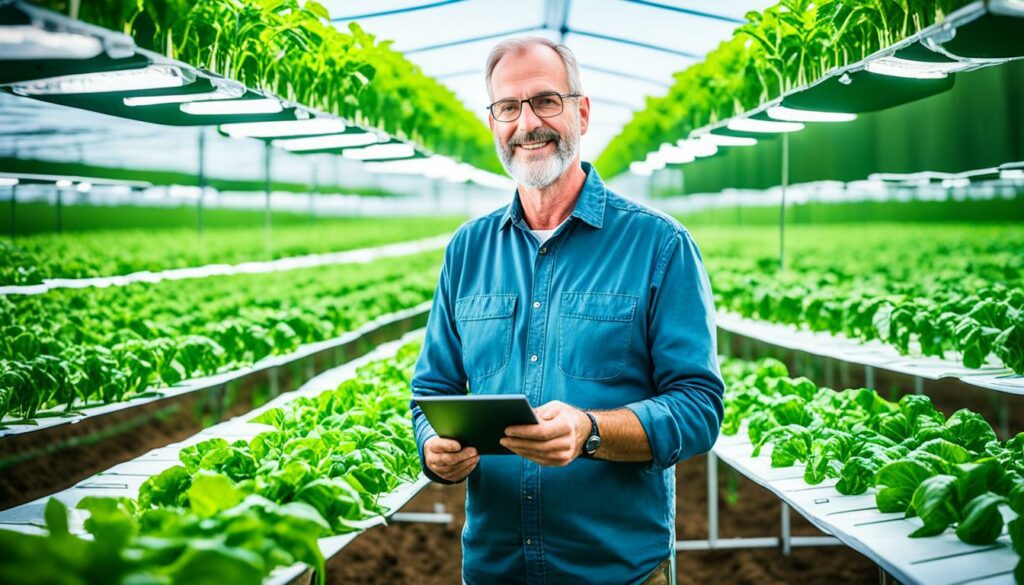

One important part of data analysis is looking at things like soil types, how much moisture is in the ground, and weather forecasts. This knowledge lets farmers create the best conditions for their crops to grow. Using precise techniques, farmers can manage their fields better. This leads to less waste and more crops.
Moreover, tools like remote sensing, drones, and predictive analytics give very detailed insights. They help farmers watch their crops closely and deal with problems fast. For example, farmers can predict when pests might attack, diseases might spread, or when bad weather is coming. This helps them prepare better and reduce risks.
By using data smartly, farmers can do better with their resources like labour, water, and supplies. This not only boosts their yields but also helps the environment. In short, data analysis is key to the future of farming. It makes farming stronger, smarter, and kinder to the planet.
Managing resources well in farming relies more and more on using advanced data analysis. With the help of farming data, farmers can work more efficiently, cut down on waste, and ensure they’re farming in a way that lasts. This means better use of resources and looking after the environment.
Water management in farming is key for farms to continue in the long term. Thanks to data analytics, farmers use information from sensors and satellites to water their fields precisely. They can see how moist the soil is at any time and give water where it’s most needed. This saves water, keeps the crops healthy, and makes farming more sustainable.
When it comes to running a farm well, optimising labour in agriculture is crucial too. Farmers can check on how workers and machines perform. With this data, they can decide when to do certain tasks to make the most of their time and resources. This effective planning helps in planting and harvesting at the right time, making work more productive and less costly.
Using farm management systems with data analytics offers a full package for making farming sustainable and efficient. It shows how modern technology has a big part to play in agriculture today.
| Aspect | Traditional Approach | Data-Driven Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Water Management | Manual scheduling, frequent overuse | Real-time monitoring, precision irrigation |
| Labour Usage | Static assignments, inefficiency | Optimised tasks scheduling, increased productivity |
| Equipment Maintenance | Reactive repairs, downtime | Predictive maintenance, optimal uptime |
Farm data analytics boosts sustainable farming and makes farms more profitable. It helps farmers plan when to plant, manage water use, and make the best use of land. This is crucial for dealing with the effects of climate change, like extreme weather.

Data analytics lets farmers be more precise in how they farm. This means using the right amount of water and fertiliser, which can lead to bigger harvests. It also helps predict and prevent problems, like bugs damaging crops and bad weather wrecking fields.
Looking at market data helps farmers know what consumers want. It guides choices on what to grow, when to grow it, and how to spend money wisely. Following these strategies not only makes farms more profitable, it also helps protect the environment.
Using data helps farmers follow rules and take care of the land better. It tracks what they do and suggests ways to improve, making farms more efficient. Plus, it encourages teamwork among farmers and experts, spurring new ideas in agriculture.
Decision support systems are changing how farmers work today. They use data from sensors, weather stations, and market info. This helps farmers make better, faster decisions. Let’s explore how DSS are improving agriculture.
Decision support systems have several parts. These parts gather and study lots of data. The main parts are:
Using decision support systems has lots of good points for farms:
Advanced DSS are making farms not only more productive but also greener. They help farmers work better and smarter.
Agricultural data analytics is moving forward at a fast pace. It’s making farming smarter and more efficient. The mix of these new technologies gives us key insights, improving farming around the world.
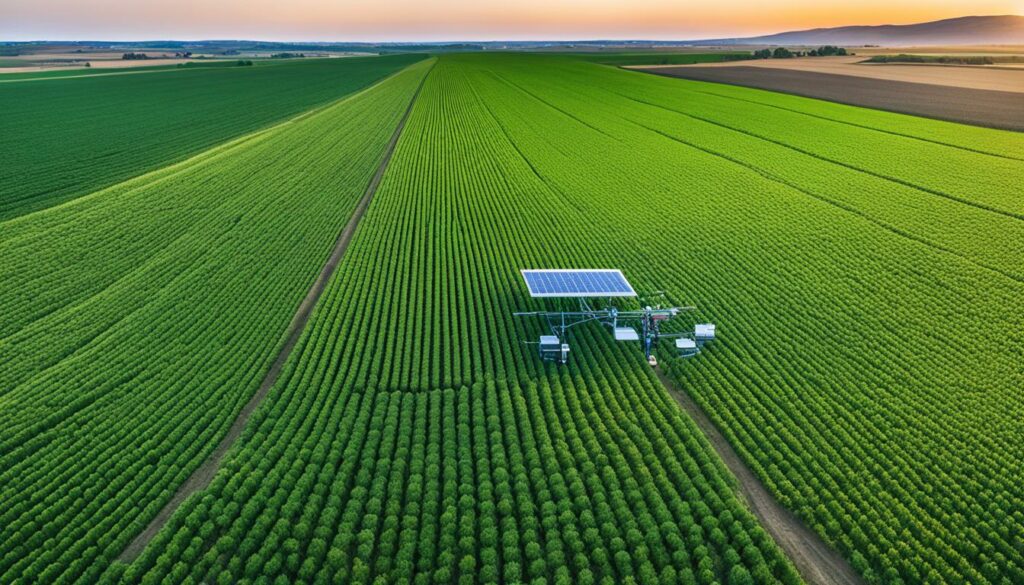

IoT is changing the game in farming. Tools like soil sensors and weather stations give us tons of data. This data helps farmers look at their fields in real-time. It makes managing fields and resources better.
Precision agriculture uses information like satellite images and soil data. It makes sure crops get the best care and predicts issues. About 80% of farms use this method now. It shows how important it is to combine IoT and big data in farming.
AI is a big deal in farming’s future too. It looks at past data to warn about future problems. For instance, it can predict pests or weather issues. This helps farmers prepare and get better harvests.
AI also brings in automated tools like self-driving tractors and drones. These machines help with tasks and look over crops. They make farm work more efficient and tackle worker shortages. This change to AI in farming can help fight against lower crop yields due to climate change.
In the end, IoT, big data, and AI are shaping the future of farming. These steps make farming smarter and stronger. They ensure food production stays sustainable and helps in facing food security issues.
Farm data analytics is changing the game in farming. It helps farmers make smart choices that boost sustainability and production. Using technologies like DSS and AI with old methods is leading to more efficient and strong agriculture.
The benefits of data analytics are clear from picking the right crops to managing pests. With data on weather, soil, and plant health, farmers can do things better. They waste less, improve their yields, and face changes in the weather and market better.
Looking ahead, combining IoT, big data, and AI opens up huge chances for farming. This will make farming more precise, secure our food worldwide, and help agriculture grow. It prepares us for the future, making sure farming can overcome the tough challenges of the 21st century.
Farm data analytics collects and analyses data on weather, soil, and crops. This helps farmers make wise choices based on facts. It improves how farmers use resources, leading to better results.
Agriculture has moved from old ways to modern, data-driven methods. Now, farmers can assess which crops or machinery work best. This leads to smarter choices and more productivity.
Using data to make decisions in farming offers many advantages. It allows for detailed crop plans and efficient risk management. This way, farmers can increase their harvests and use resources better.
Weather, soil, and crop data are key for managing farms. Weather data shows temperature and rainfall. Soil data helps know what nutrients are in the ground. Crop data looks at how much is harvested and its health. All these types are vital for making good farm decisions.
Data in farming is collected by sensors, drones, and satellites. Sensors pick up what’s happening in the fields. Drones take detailed pictures from above. Satellites cover large areas and map them out.
To get reliable data, it must be cleaned and integrated. This means making sure it’s accurate and in a usable form. Outliers are removed, and the data is checked. It ensures analysis gives the right results.
Predictive analytics uses statistics and machine learning to guess future trends. It lets farmers see what may happen with prices or harvests. This helps in planning for the future and using resources wisely.
Algorithms like linear regression and artificial neural networks figure out crop yields. They look at data to find patterns. This helps farmers make smart decisions and get better harvests.
Bad weather, pests, and market changes are big risks for farmers. Data analytics and machine learning can help predict and prevent these risks. It gives farmers ways to stay profitable and sustainable.
Monsanto uses data and satellite images for better farming. They show how data can up harvests, cut risks, and run farms more efficiently.
Data analysis shows how soil and moisture affect crops. By understanding these effects, farmers can grow crops better. This leads to more yields and smarter farming.
Data analytics helps farmers use water, workers, and machines better. It guides on when to water crops or do work. This leads to saving time and money.
Farm data analytics makes farming greener and more profitable. It uses data for better decisions and efficiency. This helps in protecting the environment, making money, and facing challenges.
Decision Support Systems help farmers collect and analyse data. They offer better decision-making and predict yields. This means managing resources better.
The future of farming data analytics will see more IoT and AI. These are set to make farming smarter, with bigger harvests and a stronger response to challenges.